Many of the plume related
risk management decisions related to the Eyjafjallajökull
volcano have been based upon observation and analysis of
Aqua and
Terra satellite images using MODIS (the
Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) and AIRS (
Atmospheric Infrared Sounder) . MODIS captures daily visible and infrared earth
imagery and provides daily images of the volcanic plume. AIRS and MODIS contain
sulfur dioxide (SO2) absorption channels that enhance
volcanic ash detection. ( See http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/iceland-volcano-plume.html ).
On a related note, here's an interesting link to a volcanic downwind
eruption cloud model: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/hysplitash-bin/dispsrc.pl
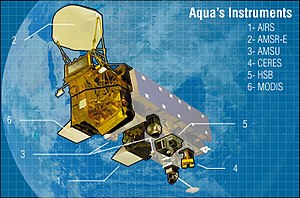 Image via Wikipedia
Image via Wikipedia Image via Wikipedia
Image via Wikipedia
No comments:
Post a Comment